R-Squared reflects the percentage of a portfolio's movements that can be explained by movements in its benchmark. An R-squared of 100 indicates that all movements of a portfolio can be explained by movements in the benchmark. A low R-squared indicates that very few of the portfolio's movements can be explained by movements in its benchmark index.
An R-squared measure of 35, for example, means that only 35% of the portfolio’s movements can be explained by movements in the benchmark index. R-squared should be used to determine the significance of the beta value. Generally, a higher R-squared will indicate a more reliable beta figure. If the R-squared is lower, then the beta is less relevant to the portfolio’s performance.
See the related definition for Standard Deviation.
The Calculation
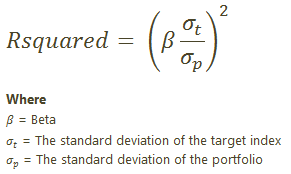
When R-Squared uses Net or Gross Returns
On the Account Analytics report, you can control whether the calculation uses net or gross with Show Returns As (Net or Gross).
When you run composites, the Composite Statistics report reports only on gross returns. For more information, see Composite Statistics.

