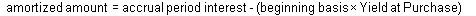# | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
The Scientific Method calculates an adjustment schedule from the acquisition date to the redemption date, extracting the per period amounts from this schedule. The premium amount is adjusted across the life of the bond using the Yield at Purchase rate. You can use this method only for fixed income securities.
Advisor View uses this formula for amortized amount per period:
Mortgage-Backed Cost Basis Adjustment Equations
The goal of the cost basis adjustment logic is to ensure that a mortgage-backed security holding’s cost basis will be adjusted each period such that at the security’s maturity date the holding’s cost basis is reduced to zero.
With only the return of principal transactions, the cost basis will not be adjusted periodically down to zero. This is because the return of principal is only adjusting based upon the par value of the security. In order to get the correct draw-down, the initial cost basis (aka “clean price”) of the bond must be used, not the par value. Thus, additional “amortization” values must be calculated and applied to correctly adjust the holding cost basis for each payment period.
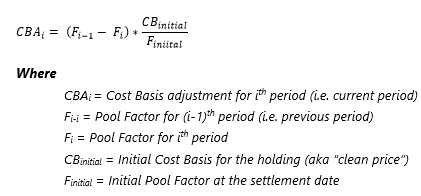
Equation: Cost Basis Adjustment
This is the total cost basis adjustment that should be applied within the coupon period.
Equation: Return of Principal
This is the value of the periodic return of principal transaction that is based upon just the par value of the security.

Equation: Additional Adjustment (aka “Amortization”)
The amortization is the difference between what is currently being recorded for the cost basis adjustment via the return of principal transaction and the actual periodic cost basis adjustment. This is the value that Advisor View is calculating.
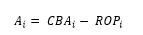
Equation: Custodian Cost Basis Adjustment Values
These equations do not exactly match every custodians calculated values for cost basis adjustment:
-
Schwab. Schwab makes amortization adjustments to cost basis on the stated coupon payment dates. Adjustments will be made to the premium paid on a fixed income security up to the amount of the stated (coupon) interest payment for the current tax year. Additional premium over the amount of the stated interest payment is carried over to the following tax year.
-
Fidelity. Fidelity does calculate the full periodic cost basis adjustment; however, it adjusts the initial factor (Finitial) in some way that appears to be related to the number of days within the coupon period that the holding settles.
-
TD Ameritrade Institutional. TD Ameritrade Institutional does not appear to calculate the full periodic cost basis adjustment. It simply reduces the cost basis by the return of principal value.